Architecture
1. Basic Architecture
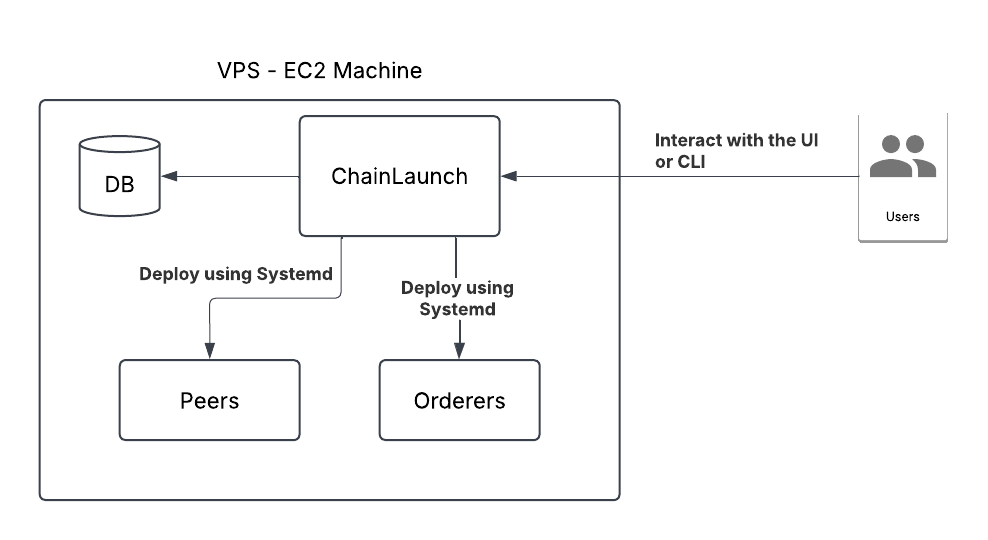
Main Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| VPS - EC2 Machine | The overall hosting environment (likely Amazon EC2 virtual private server) |
| ChainLaunch | The core application that manages blockchain deployments |
| DB | Database that stores configuration and state information |
| Peers | Blockchain network nodes that maintain and validate the distributed ledger |
| Orderers | Components responsible for transaction ordering and block creation |
| Users | End users who interact with the system through UI or CLI |
Key Relationships
- The entire system runs on a VPS/EC2 machine infrastructure
- ChainLaunch is the central component that coordinates deployments
- ChainLaunch connects to a database for persistent storage
- ChainLaunch deploys both Peers and Orderers using Systemd
- Users interact with ChainLaunch through either a user interface (UI) or command-line interface (CLI)
This appears to be a deployment architecture for a blockchain system, possibly based on Hyperledger Fabric (given the presence of Peers and Orderers, which are typical Fabric components). The system uses Systemd for service management to deploy and manage the blockchain components.
2. Module architecture
ChainLaunch is a blockchain deployment and management platform with a modular architecture designed for flexibility, reliability, and cross-platform compatibility. The system enables deployment of various blockchain networks including Hyperledger Fabric, Besu, and other blockchain frameworks through a unified interface.
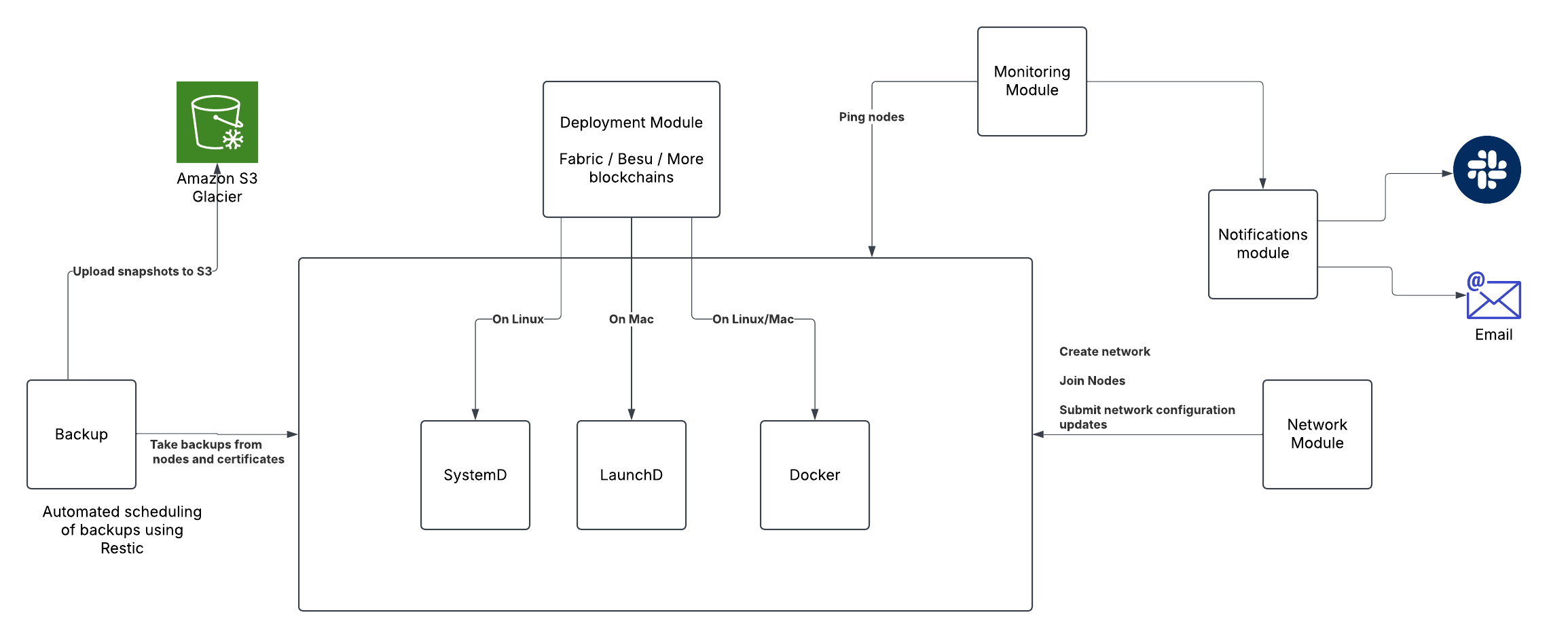
2.1 Deployment Module
This central module handles the deployment of blockchain networks across different platforms.
Supported Blockchains:
- Hyperledger Fabric
- Hyperledger Besu
- Additional blockchain frameworks
Deployment Methods:
- SystemD (Linux environments)
- LaunchD (macOS environments)
- Docker (Cross-platform: Linux/macOS)
The deployment module interfaces with the appropriate system service manager based on the host operating system, ensuring consistent deployment across heterogeneous environments.
2.2 Backup Module
Provides comprehensive data protection for blockchain network components.
Key Features:
- Automated backup scheduling via Restic
- Node state snapshots
- Certificate and cryptographic material preservation
- Direct integration with Amazon S3 Glacier for long-term, cost-effective storage
Backups are systematically collected from network nodes and associated certificates, then uploaded to S3 storage, ensuring data durability and disaster recovery capabilities.
2.3 Monitoring Module
Continuously tracks the health and performance of the blockchain network.
Functionality:
- Node availability monitoring through ping operations
- Performance metrics collection
- Anomaly detection
- Integration with the Notifications module for alerts
2.4 Notifications Module
Manages alerts and communications regarding network status.
Communication Channels:
- Slack integration for team notifications
- Email alerts for critical events
- Customizable notification rules and thresholds
2.5 Network Module
Handles blockchain network configuration and management.
Capabilities:
- Network creation and initialization
- Node joining and management
- Configuration updates and propagation
- Network topology management
2.6 Syste m Integration
The modular design allows components to operate independently while maintaining coordinated functionality through well-defined interfaces. Key integration points include:
- The Monitoring module triggers the Notifications module when issues are detected
- The Network module submits configuration updates to the Deployment module
- The Backup module interfaces with both network nodes and cloud storage
2.7 Cross-Platform Compatibility
ChainLaunch achieves cross-platform operation through:
- Platform-specific deployment mechanisms (SystemD, LaunchD, Docker)
- Abstraction layers that normalize platform differences
- Containerization for consistent environments where appropriate
2.8 Storage and Persistence
- Network configurations and state information stored in a database
- Backups preserved in Amazon S3 Glacier for long-term retention
- Local caching for performance optimization
3. Deployment diagram
The deployment diagram illustrates the complete node deployment workflow in ChainLaunch across both Linux and macOS operating systems. The process begins with a platform check that branches into two main paths:
For Linux systems, deployment utilizes SystemD services. This involves creating and configuring a .service file with working directory specifications, environment variables, resource limits, and restart policies. The service is then enabled and started through systemctl commands.
For macOS systems, deployment leverages LaunchD services. This path involves creating a .plist file configured with working directory settings, environment variables, standard I/O handling, and load-time behavior. The service is then loaded and started using launchctl commands.
Both deployment paths share common configuration requirements, including network settings, key and certificate management, chain data storage location, and log directory setup. The entire system operates within a standardized directory structure under ~/.chainlaunch/, containing dedicated directories for peers, orderers, and Besu nodes.